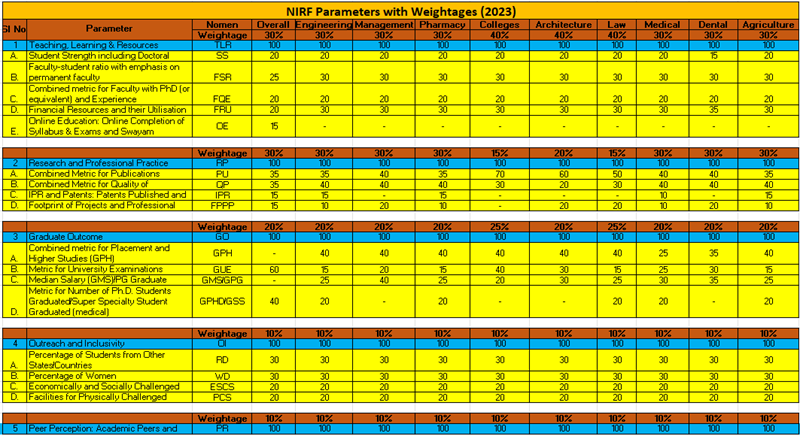
The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) employs a set of well-defined parameters to evaluate and rank higher educational institutions in India. These parameters are designed to cover all essential aspects of institutional performance, ensuring a holistic assessment. Understanding these parameters and their significance can provide deeper insights into how NIRF drives excellence in higher education.
Teaching, Learning, and Resources (TLR)
The TLR parameter is fundamental to the NIRF ranking system, focusing on the core aspects of education delivery. It includes metrics such as:
- Student Strength including Doctoral Students (SS): This metric evaluates the total number of students enrolled, including those pursuing doctoral studies, reflecting the institution’s capacity and appeal.
- Faculty-Student Ratio (FSR): A lower ratio indicates better individual attention and mentoring for students.
- Faculty with PhD and Experience (FQE): This metric assesses the qualifications and experience of the faculty, highlighting the quality of education and mentorship available.
- Financial Resources and Utilization (FRU): Efficient use of financial resources is crucial for maintaining and improving educational standards.
By focusing on these metrics, NIRF ensures that institutions prioritize quality teaching, adequate faculty, and optimal resource utilization.
Research and Professional Practices (RP)
Research is a critical component of higher education, and NIRF evaluates it through metrics like:
- Publications (PU): The volume and quality of research publications reflect the institution’s research output.
- Quality of Publications (QP): High-quality research papers published in reputed journals enhance the institution’s reputation.
- IPR and Patents (IPR): The number of patents filed and granted showcases the institution’s innovation capabilities.
- Footprint of Projects and Professional Practice (FPPP): This metric assesses the impact and scope of research projects and professional practices.
These metrics drive institutions to foster a robust research culture, encouraging innovation and contributions to various fields of study.
Graduation Outcomes (GO)
Graduation outcomes measure the success of students after completing their education. Metrics include:
- University Examinations (GUE): The performance of students in university exams indicates the effectiveness of the teaching-learning process.
- Ph.D. Students Graduated (GPHD): The number of Ph.D. graduates reflects the institution’s ability to produce high-level scholars and researchers.
By evaluating these outcomes, NIRF ensures that institutions focus on delivering education that leads to successful career paths and further studies.
Outreach and Inclusivity (OI)
Diversity and inclusivity are essential for a rich educational experience. NIRF assesses this through:
- Regional Diversity (RD): The percentage of students from other states and countries indicates the institution’s appeal and inclusivity.
- Women Diversity (WD): The representation of women in the student body and faculty highlights gender inclusivity.
- Economically and Socially Challenged Students (ESCS): This metric assesses the support provided to students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Facilities for Physically Challenged Students (PCS): Ensuring accessibility for physically challenged students reflects the institution’s commitment to inclusivity.
These metrics ensure that institutions create an inclusive environment that supports diverse student needs and promotes equal opportunities.