The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) was introduced by the Ministry of Education (MoE) in India in 2015. This framework aims to assess and rank higher educational institutions across the country, providing a transparent and reliable performance evaluation system. Launched on September 29, 2015, by the then Minister of Human Resource Development, NIRF outlines a comprehensive methodology that ensures institutions are judged based on multiple parameters that reflect their overall performance and quality of education.
The NIRF ranking methodology is grounded in five key parameters: Teaching, Learning, and Resources (TLR); Research and Professional Practices (RP); Graduation Outcomes (GO); Outreach and Inclusivity (OI); and Perception (PR). Each parameter encompasses various metrics that together offer a holistic view of an institution’s capabilities and achievements.
Teaching, Learning, and Resources (TLR)
This parameter focuses on the core activities of teaching and learning within institutions. It includes metrics such as student strength, including doctoral students, the faculty-student ratio with emphasis on permanent faculty, and the qualifications and experience of faculty members. Financial resources and their effective utilization also form a crucial part of this parameter, ensuring that institutions are adequately funded and resources are efficiently managed to foster a conducive learning environment.
Research and Professional Practices (RP)
The excellence of an institution in teaching is closely linked to its research output and professional practices. NIRF evaluates institutions based on their research publications, the quality of these publications, patents filed and granted, and the overall footprint of projects and professional practices. These metrics ensure that institutions not only impart knowledge but also contribute significantly to advancements in their respective fields through research and innovation.
Graduation Outcomes (GO)
Graduation outcomes measure the effectiveness of the teaching-learning process by assessing the success of student’s post-graduation. Metrics under this parameter include the performance in university examinations and the number of Ph.D. students graduated. This parameter essentially reflects how well students are prepared for their professional careers and further studies, indicating the institution’s role in shaping future leaders and innovators.
Outreach and Inclusivity (OI)
This parameter emphasizes the importance of diversity and inclusivity within institutions. It considers the percentage of students from other states and countries, the representation of women, the inclusion of economically and socially challenged students, and facilities for physically challenged students. By promoting a diverse and inclusive environment, institutions can offer varied perspectives and richer learning experiences.
Perception (PR)
The perception of an institution by academic peers and employers significantly impacts its reputation. This parameter gathers feedback from stakeholders to gauge the standing of the institution in the broader educational and professional community. A positive perception indicates that the institution is well-regarded for its contributions to education, research, and societal impact.
NIRF’s annual ranking results provide a comprehensive assessment of the performance of institutions across these parameters, offering valuable insights to students, parents, and policymakers. The rankings help in identifying institutions that excel in different aspects of higher education and encourage others to strive for continuous improvement.
In conclusion, the National Institutional Ranking Framework is a vital tool in India’s education sector, promoting transparency, accountability, and excellence. By systematically evaluating institutions on diverse parameters, NIRF helps in recognizing and fostering quality education, research, and inclusivity across the country.

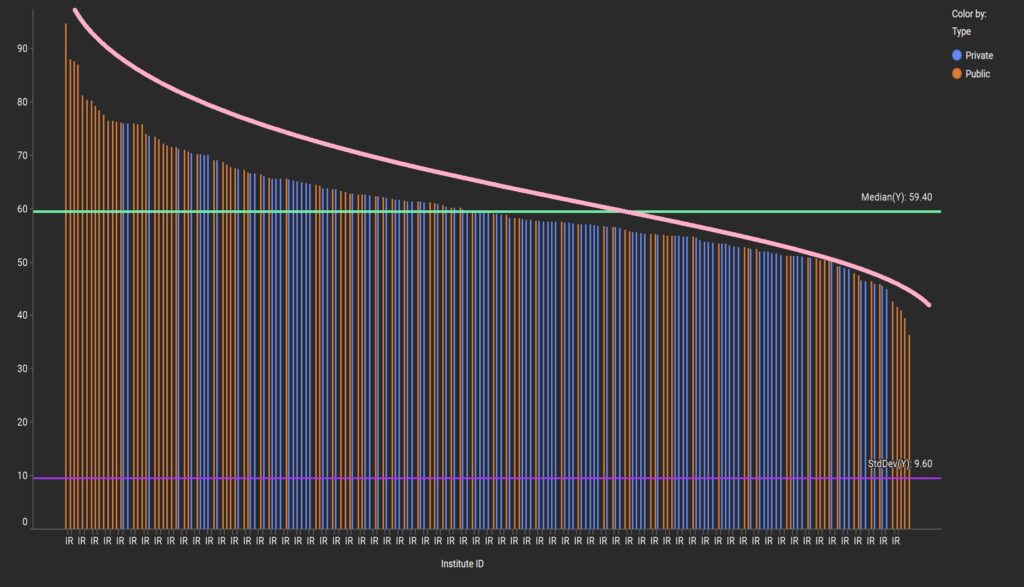
Very informative